e-Shopping List
Create Static Content
First, let’s create content that is need for our application by creating the HTML framework and then adding the static view components.
Create HTML Framework
Let’s first create a blank framework and tweak it for mobile devices if necessary.
- Open Dreamweaver, select File > New… (or CTRL+N), and in the dialog box that appears:
- ensure that the New Document option is selected
- Document Type is set to HTML
- Framework set to NONE
- Doc Type set to HTML5
- In the Title field, type e-Shopping List
- Click the Create button
WHY: To create a blank HTML framework
- Select File > Save (or CTRL+S) and in the dialog box that appears navigate to where you want to save the file. In the File name text field, type a descriptive HTML name (e-ShoppingList.html) and then click the Save button.
- If app is intended to be viewed on a mobile device, add the following highlighted code:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>e-Shopping List</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Create View
Now that we have a framework established, let’s add static view components to it.
- In between the
<body>
tags, add the following highlighted HTML code:
WHY: To create a static view of the application.
<body> <div>
NOTE: This is standard HTML code with two placeholdes (itemand erroMessage) . There is nothing dynamic here.
<h1>e-Shopping List</h1>
<input placeholder="Add shopping items here">
<button>Add</button>
<p>Press <span>X</span> to delete a shopping item.</p>
<ul>
<li><span>X </span>{{item}}</li>
</ul>
<p>{{errorMessage}}</p>
</div> </body>
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. It looks like a normal HTML page. However, if you click the Add button, nothing will happen because it has not yet been programmed.
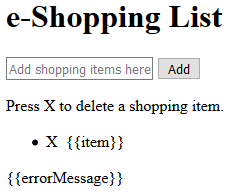
NOTE: The double curly braces {{...}} are placeholders for dynamic content that will be created later.
- Add the following styles in a set of
<style>
tags below the
<title>
tag:
<title>e-Shopping List</title> <style>
.panel { font-family:Arial;
width:250px;
background-color:lightgray;
margin:10px;
padding:10px;
box-shadow:5px 5px 5px gray;
-webkit-box-shadow:5px 5px 5px gray;
}
.list_item { cursor:pointer;
margin-left:10px;
color:red;
font-weight:bold;
}
.bullet_list { list-style-type:none;
margin-left:-50px;
}
.highlight_red { color:red; font-weight: bold; }
</style> - Add the following FIVE CSS classes:
WHY: To link them to the styles in the <style> tag and to "style" the application.
<body>
<div class="panel">
<h1>e-Shopping List</h1>
<input placeholder="Add shopping items here">
<button>Add</button>
<p>Press <span class="highlight_red">X</span> to delete a shopping item.</p>
<ul>
<li class="bullet_list"><span class="list_item">X </span>{{item}}</li>
</ul>
<p class="highlight_red">{{errorMessage}}</p>
</div>
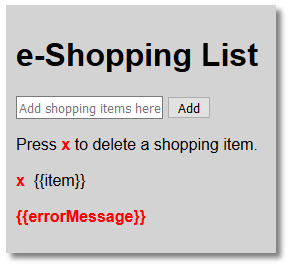
</body> - CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see the application looks better.
Create Dynamic Content
Now that we have the standard framework in place, let’s add some dynamic content.
Create App
We will start first by:
- linking the AngularJS framework to the page via a CDN link,
- using a <script> tag, we will create an app (angular.module(“eShoppingListApp”)) and then assign the app to a variable (var app)
- using the ng-app attribute (or directive) to associate the <body> tag with the app name created earlier (ng-app=”eShoppingListApp”)
Add the following highlighted SCRIPT code below the
<title>
tag and add the ng-app directive in the
<body>
tag:
WHY: To make the
<body>
tag of the HTML page an application.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>e-Shopping List</title>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.6.4/angular.min.js"></script>
<script>
var app=angular.module("eShoppingListApp", []);
</script>
<style>
.panel{
width: 250px;
background-color: lightgray;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px gray;
-webkit-box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px gray;
}
.list_item { cursor:pointer;
margin-left:10px;
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
.bullet_list { list-style-type:none;
margin-left: -50px;
}
.highlight_red{ color:red; font-weight: bold;}
</style>
</head>
<body ng-app="eShoppingListApp">
NOTE: We have just associated the <body> tag with the AngularJS framework making the <body> tag and all of its content an application. How easy was that!!!
Associate Controller with App (within the SCRIPT code)
Now that we have created an app, let’s associate it with a controller to “control” our app. We want to add the following functionality to our controller:
After entering a "shopping" item:
- if a user click the Add button, have the "shopping" item show in the list below
- if a user click the X button, delete the item
Add the following highlighted code:
WHY: To assign a controller to the app and create a products array with a few default values to the current $scope.
<script>
var app=angular.module("eToDoListApp", []);
app.controller("eShoppingListCtrl", function($scope) {
// Default Items -------------------------------------------------
$scope.products=["Milk", "Bread", "Cheese"];
});
</script>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The $scope.products is an array with three default items in it (Milk, Bread, and Cheese).
Associate Controller with App (within the HTML code)
Now that we have associated the controller with the app within the SCRIPT code, we now need to associate the SCRIPT code within the HTML code.
- Add the following highlighted ng-controller directive to the
<body>
tag:
WHY: To associate the controller with the application.
<body ng-app="eShoppingListApp" ng-controller="eShoppingListCtrl">
- Write the following highlighted ng-repeat directive in the
<li>
tag:
WHY: To iterate through the products array to create three <li> elements.
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="item in products" class="bullet_list"><span class="list_item">x </span>{{item}}</li>
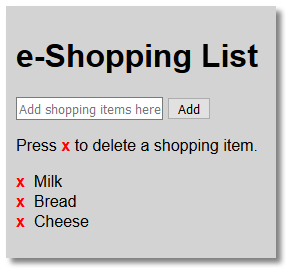
</ul> - CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see that the placeholder expression {{item}} was replaced with three bullet items. However, the placeholder {{errorMessage}} has disappeared because it is not yet defined.
Add "Add ToDo Item" Functionality
Now that we know our application is working correctly, let’s add our first functionality. We will add an "addItem" function so that if a user click the Add button it will add the "shopping" item to the list with a "x" next to it.
- Write the following highlighted code below the $scope.products statement:
WHY: To create the add function within the controller:
<script>
CODE EXPLANATION:
var app=angular.module("eShoppingListApp", []);
app.controller("eShoppingListCtrl", function($scope) {
// Default Item -------------------------------------------------
$scope.products=["Milk", "Bread", "Cheese"];
// Add function -------------------------------------------------
$scope.addItem = function(){
$scope.products.push($scope.addShoppingItem);
}
});
</script>
- The push() method of the products array is used to ADD "shopping" object to the array.
- Add the following highlighted TWO directives:
WHY: To have the input field "model" the data from the controller AND to have the Add button call (or invoke) the addItem() function within the controller.
<div class="panel">
CODE EXPLANATION:
<h1>e-Shopping List</h1>
<input ng-model="addShoppingItem" placeholder="Add shopping items here">
<button ng-click="addItem()">Add</button>
<p>Press <span class="highlight_red">x</span> to delete a shopping item.</p>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="item in products" class="bullet_list"><span class="list_item">x </span>{{item}}</li>
</ul>
<p class="highlight_red">{{errorMessage}}</p>
</div>
- The ng-model directive is used to "model" the data from the controller
- Theng-click directive is used to "listen" for a click event and when it happens call (invoke) the addItem() function.
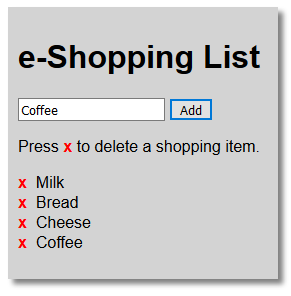
- CHECK POINT: Save the fileand preview it in a browser. Add a "shopping" item to the input field and then click the Add button. You should see that the "shopping" item gets added to the list below. Add a few more items.
Add "Remove Shopping Item" Functionality
Now that we can add items to the list, let's add code to remove items from the list.
- Write the following highlighted code within the
<script>
tag below the addItem function:
WHY: To create a function that will remove an item or items from the list when it is clicked on.
<script>
var app=angular.module("eShoppingListApp", []);
app.controller("eShoppingListCtrl", function($scope) {
// Default Item -------------------------------------------------
$scope.products = ["Milk", "Bread", "Cheese"];
// Add function -------------------------------------------------
$scope.addItem = function () {
$scope.products.push($scope.addShoppingItem);
} // Remove Item --------------------------------------------------
$scope.removeItem = function (item) {
$scope.products.splice(item, 1); }
});
</script>CODE EXPLANATION:
- The spice method of the products array is used to identify the item that need to be removed. - Add the following highlighted ng-click directive inside of the
<span>
tag inside of the
<li>
tag:
WHY: So that the ng-click directive can be used to "listen" for a click event and when it happen call (invoke) the removeItem function and use the current index ($index) as its parameter.
<li ng-repeat="item in products" class="bullet_list"><span ng-click="removeItem($index)"
class="list_item">x </span>{{item}}</li>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The $index is the current item of the li element to ascertain which element to delete. - CHECK POINT: Save your file and preview it in a browser. Add a "shopping" list item and then click the Add button. Repeat several times. Then, click one of the "x" next to a shopping item that you would like to delete. You should see that shopping item gets removed from the list. However, the item is not actually saved. To do that see section below on Local Storage.
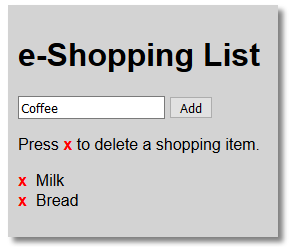
Before:

After the "x" next to Coffee and Cheese are clicked:
Handle Errors
There are several issues that need to be resolved:
- If the same item is added twice, the application will stop working.
- A user should not be allowed to add an empty item.
These problems can be resolved by adding some "if" conditional statements to check the value BEFORE adding it.
- Modify the addItem function with the following highlighted code:
// Add function -------------------------------------------------
$scope.addItem = function (){
$scope.errorMessage = "";
if (!$scope.addShoppingItem) {return;}
if ($scope.products.indexOf($scope.addShoppingItem) == -1) {
$scope.products.push($scope.addShoppingItem);
} else {
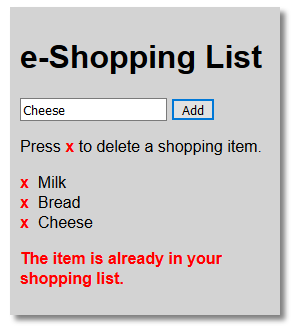
$scope.errorMessage = "The item is already in your shopping list.";
}
}CODE EXPLANTION:
- The first "if" statement checks to see if no text was entered, if so, it will return without doing anything. Notice the NOT symbol (!) in front of the $scope.
- The second "if" statement checks to see if the item has not already been added. If not, add it to the products array and display it, else assign the message "The item is already in your shopping list" to the errorMessage placeholder ($scope.errorMessage). - Modify the removeItem function with the following highlighted code:
WHY: To remove any previous error message once the "shopping" item has been removed.
// Remove Item --------------------------------------------------
$scope.removeItem = function (x) {
$scope.products.splice(x, 1); $scope.errorMessage=""; } - CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. If you try to add a shopping item that is the same, you should see a red message displayed saying, "The item is already in your shopping list." Also, if you click the Add button when no text is entered, nothing will happen.
Add Local Storage (Bonus)
See Add Local Storage for example on how to implement Local Storage.