Communicate With Server
IMPORTANT NOTICE:
This content is for informational or experimental purposes only.
If you would like to know how the db.php script was created that will be used for most pages in the project, see details below.
PHP scripts are used to send SQL statements (e.g., SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT, DROP AND CREATE) to a MySQL database to be executed and the result (e.g., retrieval, insertion, deletion, or selection of data) is returned to the PHP script or an error can be displayed if no result is returned.
Once you have connected to a server, you can then communicate with it by requesting a query and returning a result.
It is a good idea to test the database to see if it will return the desire results before writing a lot of code for the other pages.
- Add a TEST SQL to the db.php connection script:
To see if you can communicate with the server and return a result.
<?php
$host ="localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "pdo_employee_directory1234";
// Create Connection ----------------------------------------
$pdo_conn = new PDO( "mysql:host=$host; dbname=$database", $username, $password);
// Return a record set (also known as resultset) -----------
$sql = 'SELECT FirstName, LastName from employees';
// Loop through the $sql array for each row ----------------
foreach ( $pdo_conn->query($sql) as $row ){
echo $row['FirstName']." ".$row['LastName']."<br>";
}
// Close the database connection ----------------------------
$pdo_conn = null;
?>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- $sql = 'SELECT FirstName, LastName from employees'; statement is used to create a SELECT query and store it in the $sql array.
- The foreach loop is used to iterate through the $sql array for each item ($row).
- The echo command is used to display the result (FirstName LastName) of the database to the screen
- The $dpo_conn = null; statement is used to close the connection.
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see the result of the query.
Carol Green
Bob Jones
Debra Samson
Jason Taylor
Bob Anderson
Ann Ricoh
TRY/CATCH (OPTIONAL)
It is best practice to use the try/catch syntax to check if there is an error when you are attempting to connect to a database.
- Modify the code by wrapping the connect and success code in a try code block and error code in the catch block.
<?php
$host ="localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "pdo_employee_directory1234";
try {
// Create Connection ----------------------------------------
$pdo_conn = new PDO( "mysql:host=$host; dbname=$database", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode and exception
$pdo_conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
echo "<strong>Connected successfully:</strong><br>";
} catch ( PDOException $e ) {
echo "<strong>Connection failed:</strong> <br>" . $e->getMessage() . "<br>";
die();
}
// Return a record set (resultset) --------------------------
$sql = 'SELECT FirstName, LastName from employees';
// Loop through the $sql array for each row ----------------
foreach ( $pdo_conn->query( $sql ) as $row ) {
echo $row[ 'FirstName' ] . " " . $row[ 'LastName' ] . "<br>";
}
// Close the database connection ----------------------------
$pdo_conn = null;
?>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The try code block test the database connect and if an error is found, the catch code block "catch" and displays it.
- The try code block is used to check for any error. If one if found, it will be "caught" in the catch code block in the $e variable. - The catch code block is used to display a custom error message based on the $error variable that is passed into the catch() method as an argument.
- The getMessage() method is used to give the SPECIFIC type of error that can occur.
- Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see an SUCCESS message:
Connected successfully:
Carol Green
Bob Jones
Debra Samson
Jason Taylor
Bob Anderson
Ann Ricoh
- Modify the $database_username variable (or any other value in the connection string). In our case, we add a "X"
$database_username = 'CorneliusChopinX';
- Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see an ERROR message:
Connection failed:
SQLSTATE[HY000] [1045] Access denied for user
'CorneliusChopinX'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
- Remove the error and then save the file again.
WHY: To restore the connection.
$database_username = 'CorneliusChopin';
- Comment out the echo statement and the $pdo_conn for the connected successfully and the close connection. Then, comment out or delete the highlighted code as it was only used to test the database connection:
<?php $host ="localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "pdo_employee_directory1234";
try {
// Create Connection ----------------------------------------
$pdo_conn = new PDO( "mysql:host=$host; dbname=$database", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
// $pdo_conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
// echo "<strong>Connected successfully:</strong><br>";
} catch ( PDOException $e ) {
echo "<strong>Connection failed:</strong> <br>" . $e->getMessage() . "<br>";
die();
}
/* $sql = 'SELECT FirstName, LastName from employees';
// Loop through the $sql array for each row ----------------
foreach ( $pdo_conn->query( $sql ) as $row ) {
echo $row[ 'FirstName' ] . " " . $row[ 'LastName' ] . "<br>";
} */
// Close the database connection ----------------------------
// $pdo_conn = null;
?>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The lines above were commented or deleted because we want to make the PHP script generic to work for each page that we create.
- If you forgot to comment out the close connection statement ($pdo_conn = null;) the code will not work for the other pages. However, the connection should be closed in EACH of the pages separately.
- Notice the error statement IS NOT commented out because we want it to give an error when the other pages are created.
FURTHER EXAMPLES:
This content is for informational or experimental purposes only.
The examples below is used to give additional examples of what is returned from a database query. The "try/catch" block and close connection are not implemented because this is for demonstration purposes only.
- Create a new PHP file, name it db_results_examples.php, and then add the following connection script including the blank lines:
<?php
$host ="localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "pdo_employee_directory1234";
// Create Connection ----------------------------------------
$pdo_conn = new PDO( "mysql:host=$host; dbname=$database", $username, $password);
?>
- Add the following highlighted code:
WHY: To RETRIEVE a SINGLE record from the database.
<?php
$host ="localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "pdo_employee_directory1234";
// Create Connection ----------------------------------------
$pdo_conn = new PDO( "mysql:host=$host; dbname=$database", $username, $password); // Retrieve the FIRST record from the database based on the FirstName column
$pdo_statement = $pdo_conn->prepare("SELECT * FROM employees");
$pdo_statement->execute();
$result = $pdo_statement->fetch();
echo ($result["FirstName"]);
?>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The fetch() method will return a SINGLE record from the database.
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see the FIRST record of the FirstName column in the database displayed (Carol).
- Change the echo statement to read:
$result = $pdo_statement->fetch();
echo ($result["FirstName"]. " ". $result["LastName"]);
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see the FIRST record of the FirstName and LastName columns in the database displayed with a space between the two (Carol Green).
- Replace fetch() with fetchAll() and replace the echo statement with the foreach loop:
WHY: To loop through the $result array and return ALL of the records from the database.
$result = $pdo_statement->fetchAll(); foreach($result as $row) { print_r($row);
}
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The foreach loop is used to "loop" through the $result array.
- Notice the print_r() method instead of the print() method is used. The print_r() method is used to print the result of an array.
If you were to used the regular print() method, you would get the following error for each record in the database:
"Notice: Array to string conversion in C:\xampp\htdocs\EmployeeDirectory_JQM_PDO\db_results_examples.php on line 14 Array"
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see a LARGE array of objects. However, if you look carefully, the fetchAll() method get results by BOTH the key (ID, FirstName, LastName, etc.) and the index (0,1,2, etc) so the result is being repeated. This will be cleaned up in the next step.

- Add the following highlighted argument to the fetchAll() method.
WHY: To cleanup the array:
$result = $pdo_statement->fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
CODE EXPLANATION:
- PDO::FETCH_ASSOC is used to ...
- Save the file again and open it up in a browser. You should see an array of objects but this time you see a cleaner array with just key/value or name/value pairs.
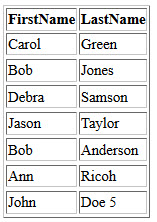
- Comment out the foreach loop that was created earlier and add the following highlighted code BELOW the previous PHP code block (after the ?>).
WHY: To create a sample table from the database results instead.
$result = $pdo_statement->fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
/* foreach( $result as $row )
{
print_r( $row );
} */ ?> <table border="1">
<tr><th>FirstName</th><th>LastName</th></tr>
<?php foreach( $result as $row )
{
echo "<tr><td>";
echo $row['FirstName'];
echo "</td><td>";
echo $row['LastName'];
echo "</td><tr>";
}
?>
</table>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The first two lines and the last line are static HTML table content.
- The nested foreach loop is used to iterate through the array and dynamically create the "rows" of the table.
- You could write the series of echo statements all of one line to see the HTML table structure (e.g., <tr><td>...</td><td>...</td></tr>) better:
echo "<tr><td>"; echo $row['FirstName']; echo "</td><td>"; echo $row['LastName']; echo "</td><tr>";
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see a sample table created with two table headers. More headers could have been added.
- Add the following code BELOW the closing
</table>
tag:
</table> <ul>
<?php foreach($result as $row)
{ echo "<li>";
echo $row['FirstName'];
echo " ";
echo $row['LastName'];
echo "</i>";
}
?>
</ul>
CODE EXPLANATION:
- The first and last lines are static HTML unordered list content.
- The nested foreach loop is used to iterate through the array and dynamically create the <li> tags for the bullet list.
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see a sample bullet list created.

- Add the following code BELOW the closing
</table>
tag:
WHY: To get a SPECIFIC record from the database based on its index
</ul> <?php echo ($result[2]["FirstName"]); echo(" "); echo ($result[2]["LastName"]);
?>
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see a SPECIFIC record from the database displayed based on its index value. (e.g., Debra Samson).
- Add the following code BELOW the last PHP script:
WHY: To get the total number of records from the database.
?> <?php
$count = $pdo_statement->rowCount();
print("<h1><br>Total Records: <strong> $count</strong> </h1>");
?>
- CHECK POINT: Save the file and preview it in a browser. You should see the total number of records returned from the database:
Total Records: 7